
IgY purification kit
Product code: EYK-FF KIT
PRICE: 300 EUR/KIT
KIT CONTENT
|
INSTRUCTION FOR USE, Purification of IgY
- Equilibrate the column with 20 ml of IgY Binding Buffer (BBY).
- Add such a crude egg yolk prepared in point 1 to 25 ml of IgY Loading Buffer (Code: LBY) and 20 ml of IgY Binding Buffer (BBY). Mix for 1-2 minutes to obtain a solution.
- Centrifuge the falcon of IgY Binding Gel (Code: EYK-FF). Discard the supernant from the gel cake.
- Add the solution of egg yolk prepared in point 2 to the falcon containing the gel cake prepared in point 3. Mix gently the suspension for 30 minutes at 4°C.
- Centrifuge at 3000 g and dicard the supernant from the gel cake.
- Add 40 ml of IgY Binding Buffer (BBY). Centrifuge and discard the supernatant. Repeat thrice more the same operation.
- Add 50 ml of IgY Elution Buffer (Code : EBY) and centrifuge. Collect the IgY supernant.
- Assay the elution fractions obtained as described in point 7, using the most appropriate system (SDS-PAGE, immunodiffusion, radioimmunoassay, Elisa...)
SDS-PAGE 12% in the presence of beta-mercaptoethanol
(Stained with Coomassie blue)
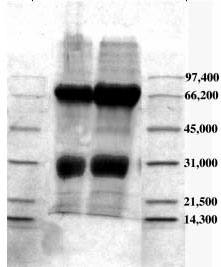
Lanes 2 & 3: purified by Affiland Egg yolk IgY purification kit.
Lanes 1 & 4: Markers.
It is recommended to regenerate the gel after every 5 cycles of use.
- Wash the column with 10x volumes of NaOH 0.1M.
- Wash the column with 10x volumes of distilled water.
- Equilibrate the column 10x volumes of PBS (50 mM K2HPO4, 150mM NaCl) pH 7.4.
- Store the column at 4°C in the presence of NaN3 0.1% (w/v).
- For the next use, see INSTRUCTION FOR USE as described above.
STERILE REGENERATION OF THE SHEEP IgY BINDING GEL
(GEL SANITIZATION)
AFTER EVERY 5 CYCLES OF USE
- Wash the column with 5 volumes of acetic acid 1 M.
- Wash the column with 10 volumes of sterile distilled water.
- Wash the column with 5 volumes of NaOH 1M.
- Wash the column with 10 volumes of sterile distilled water.
- Wash the column with 10 volumes of PBS (50 mM K2HPO4, 150mM NaCl) pH 7.4; NaN3 0.1%(w/v).
- The sterile gel column is now ready to be re-used.
ADVANTAGE OF BIRD IgY
Many mammalian proteins including human proteins have proven to be poorly or not at all antigenic in mammalian animal hosts. The explanation is due to the resemblance in structure of mammalian proteins between species.
The birds (chickens, turkeys...) are not mammals. The immunoglobulin in hen eggs which is the same in its serum, is named IgY. The production of specific antibodies in birds presents many advantages as shown below.
Mammalian
IgG<COMPARISON>
Bird (Chicken, Turkey...)
IgY
Sometimes very poor avidity
Mammalian antigens1 / response
High avidity
Yes
Protein A & Protein G5a / binding
No
Yes
Common Fc receptorMammalian IgG5 / recognition
No
Yes
Mammalian complements5b / recognition
No
From 60th day in rabbits
Antibody response4
From 30th day
50-70 ml sera/90
immunization days:
500-700 mg of IgGAntibody production capacity2
1 egg per day and 60 eggs/90
immunization days:
3-6 g of IgY
Antisera: expensive work
(bleeding, centrifugation, conservation at -20°C or lower temperature)Antibody source collection3,6
Eggs: cheaper work
(the eggs can be stored at 4°C for at least 6 months without loss of egg yolk quality)
RIA, IRMA, ELISA, CONJUGATE, ENZYMATIC DIGESTION...
Applications7
RIA, IRMA, ELISA, CONJUGATE, ENZYMATIC DIGESTION...
1 The birds recognise easily the presence of any mammalian proteins. The specific antibodies IgY developed in chickens therefore get high avidity to mammalian antigens.
2 Furthermore, the quantity of IgY in one egg yolk is appreciable (easily 50-100 mg) and the hen can lay one egg per day.
3 The birds are easy to feed in comparison with mammalian animals (rabbits, sheep, goats...), resulting in lower production cost. The collection of eggs is much easier than collection of mammalian serum.
4 The response for specific antibody in birds is much quicker than in mammalian animals: from 30th day in chickens, from 60th day in rabbits and longer in bigger mammalian animals.
5 The IgY (MW: 180,000 daltons) is different from mammalian IgG (MW: 150,000 daltons) as well as their Fc. This results in:
5a IgY does not recognise mammalian Fc receptors. It doesn't bind to Protein A and Protein G.
5b IgY does not recognise mammalian complements.
7 Finally, all applications carried out with IgG can be realized with IgY: RIA (radioimmunoassay), IRMA (immuno-radio-metric assay), ELISA (enzyme linked immuno sorbent assay)... or digestion by papain and trypsin for getting Fab and Fab'.
References:
Akita EM, Nakai S; J Immunol Methods 1993 Jun 18; 162 (2), 155-64.
Carlander D et al.; Ups J Med Sci 1999; 104 (3), 179-89.
Gassmann et al.; FASEB J 1990 May; 4 (8), 2528-32.
Gassmann et al.; Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd 1990; 132 (6), 289-94.
Higgins DA et al.; Vet Immunol Immunopathol 1995 Jan; 44 (2), 169-80.
J Dairy Sci 1998 Jan; 81 (1), 54-63.
Larsson A et al.; Poult Sci 1993 Oct; 72 (10), 1807-12.